10 SCIENCE REVISION NOTES
CHAPTER 1 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS
All living structures are carbon based. The earth's crust has only 0.02% of carbon in the form of carbonates, coal and petroleum. The atmosphere has 0.03% of carbon. Carbon compounds are used extensively in manufacturing different useful materials.
Covalent bond in carbon
★ Carbon cannot form C4- anion, because the nucleus cannot hold on to ten electrons, i.e., extra four electrons.
★ Carbon cannot form C4+ cation, because it requires a large amount of energy to remove four electrons, leaving behind six protons to hold just two electrons.
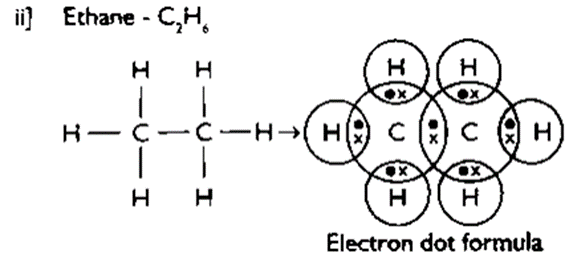
★ To overcome both the above problems, carbon forms covalent bonds with other elements by sharing its valance electrons.
Covalent bond in Hydrogen molecule
Covalent bond in Oxygen molecule
Covalent bond in Nitrogen molecule
Formation of Methane molecule
In this process carbon shares its four electrons with four hydrogen atoms to form methane.
Properties of Carbon
Carbon compounds are poor conductors of electricity. They are insoluble in water. They do not give rise to ions. They have low melting and boiling points. Covalent compounds have strong bond within the molecule but the inter-molecular forces are weak.
Versatile nature of carbon
i] Catenation: The ability of carbon to form bonds with other carbon atoms to give long chain molecules is called catenation. There are three types of catenation.
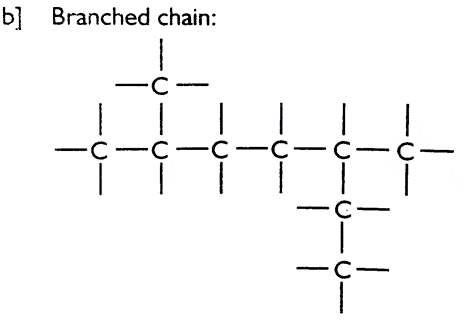
ii] Tetra valency: Carbon shows valency 4. It forms covalent bond with four hydrogen atoms to form methane.
C+2H₂→ CH, (Methane)
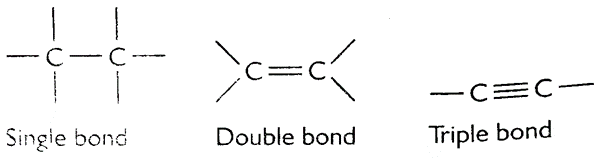
iii] Carbon forms single, double and triple bonds with other carbon atoms.
Organic Chemistry
The branch of chemistry which deals with carbon and its compounds is called organic chemistry.
Saturated carbon compounds
Carbon compounds which have only single bond between their carbon atoms are called saturated carbon compounds.









No comments:
Post a Comment