10 SCIENCE REVISION NOTES
CHAPTER 1 CHEMICAL REACTIONS AND EQUATIONS
★ Based on chemical properties substances are classified as Acids, Bases and Salts.
★ Acids prepared from minerals are called mineral acids
Examples: Hydrochloric acid - HCI, Sulphuric acid - H2SO4, Nitric acid - HNO3
★ Acids present in plants and animals are called organic acids
Examples: Lemon -citric acid, Tomato - oxalic acid, Tamarind - tartaric acid, Ants - Formic acid
★ Some other organic acids are:
Methanoic acid - CH3COOH
Ethanoic acid - C2H5COOH
Benzoic acid - C6H5COOH
Formic acid - HCOOH
Indicators: An indicator is a dye that changes colour when it is put into an acid or a base
Types of indicators:
→ Natural indicators - Examples: litmus, turmeric, cabbage etc.
→ Synthetic indicators - Examples: phenolphthalein, methyl orange.
→ Olfactory indicators - Examples: Onion, vanilla, clove
→ Universal indicator - It is a mixture of several indicators
Properties of Acids:
→ Acids are sour to taste.
→ They turn blue litmus to red
→ Acids have hydrogen ions
→ They conduct electricity.
→ Acids react with bases to form salt and water.
→ Sulphuric acid reacts with zinc metal and liberates hydrogen gas.
When a candle is introduced into a soap bubble containing hydrogen gas, 'popping' sound is heard with a small explosion, indicating the gas liberated is hydrogen.
Zn(s)+H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) +H2(g)
Note: Metals displace hydrogen from acids. All compounds which contain hydrogen are not acids
→ Hydrochloric acid reacts with metallic carbonate and metallic hydrogen carbonate to give carbon dioxide and sodium chloride.
Na2CO3 + 2HCI → 2NaCI + H2O + CO2
NaHCO3 + HCI → NaCI + H2O + CO2
To know that CO, is liberated, pass the gas through lime water; where lime water turns milky.
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2(g) → CaCO3(s)+H2O(l)
lf excess CO, is passed, then the following reaction takes place
CaCO3(s) + H2O (l) + CO2(g) → Ca(HCO3)2
→ Reaction with metallic hydroxides:
2NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(q) → Na2SO4(aq) +2HO(l)
Ca(OH)2(aq) + 2HCI(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
→ Neutralisation reaction: When an acid reacts with a base, salt and water are formed. This reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
NaOH (s) + HCI(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Ca(OH)2 + H2SO4 → CaSO4 + 2H2O
→ Conduction of electricity by acids:
When an acid dissolves in water it gives hydrogen (H+) ions or hydronium ions (H3O+ ). Because of the formation of these ions acids conduct electricity in aqueous solution.
HCI → H+ + CI- (H+ hydrogen ion)
H+ + H2O → H3O+ (H3O+ hydronium ion)
Note:
→ Organic acids are non-conductors of electricity as they do not dissociate into ions
Examples: Formic acid - HCOOH, Methanoic acid - CH3COOH, Ethanoic acid - C2H5COOH
→ Dilution of an acid is an exothermic reaction. Therefore acid is to be added slowly to water taken in a beaker with constant stirring. Suddenly adding acid to water causes splashing the acid which can cause burning of the skin In dilution of acids or bases H+ or OH- ions decrease per unit volume.
Properties of Bases:
→ Bases are bitter to taste.
→ Bases dissolve in water. A base which dissolves in water is called alkali.
→ Bases turn red litmus to blue.
→ Bases when dissolved in water give hydroxide ions (OH- ions).
→ Bases react with acids to give salt and water.
2NaOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → Na2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
KOH(aq) +HCI(aq) → KCI (aq) + H2O(l)
→ Bases conduct electricity in their aqueous solution
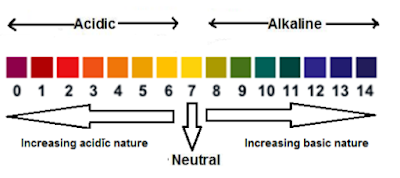
pH Scale and pH Value:
→ The strength of an acid or a base is measured on a scale of numbers having values from 0 to 14. This is called pH scale and the numbers are called pH values.
→ pH has no units. It is a value which indicates how strong is an acid or a base.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
NaCI + H2O + CO2 + NH3 → NH4CI+ NaHCO3
NaHCO3 + H+ (from an acid) → CO2 + H2O + sodium salt of acid
Na2CO3 + 10H2O → Na2CO3.10H2O
CaSO4.2H2O → CaSO4. ½ H2O + 1 ½ H2O

No comments:
Post a Comment