Class 6th Science Notes
Chapter 10 Motion and Measurement of Distances
Transport
→ It is a mechanism in which a thing is carried from one place to another.
Transport system evolution
→ In the earlier times, land transport was done using animals or human backs, while, water transport was done on hollow wooden logs or simple wooden boats.
→ After the invention of wheel, bullock carts, camel carts were developed.
→ Transport then evolved in the 19th and 20th century to bus, trains, cars, and airplane, jets, steam and motor boats, etc.
Distance
→ It is length of the space between two points or between two places is called distance.
→ Example: If the two points are close by, the distance between them will be small otherwise if the two points are far off, then the distance between them will be large.
Length
→ Length tells us how long an object is.
→ Measurement is comparison on an unknown quantity with a known quantity. The known quantity is called Unit.
→ Measurement consists of two parts, a number (quantity) and a unit.
→ Depending upon the unit, the number changes.
Standard Units of Measurements
→ Scientists all over the world have accepted a set of standard units for measurements. This system of units is called International System of Units (SI units).
Needs for standard units of measurement
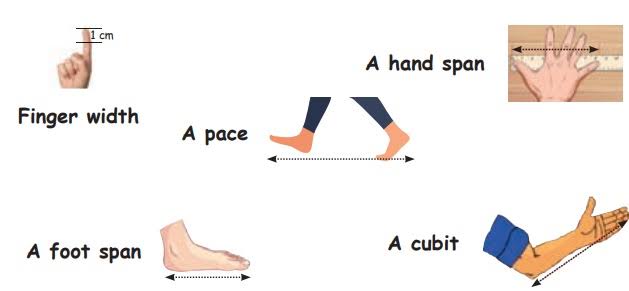
→ Units like foot, hand span, cubit, footstep etc., vary.
→ They depend upon the size of an individual, hence such units cause confusion in measurements.
→ Example: length-meter, time-second, mass- kilogram.
Rules for writing symbols of units
→ Units are usually written in small letters
→ It is not given in plural form
→ It is not followed by a full stop unless it is at the end of the sentence.
Measuring Length of a Curved line
→ Instead of straight scale using measuring tape for the measurement of curved line or surface.
Motion
→ Any change in position with time can be termed as motion.
→ A motion can be termed as slow or fast based on the distance it covers in a specific amount of time.
→ The objects which are not moving are said to be at rest.
Classification of motion on the basis of the path they follow
(i) Rectilinear Motion : Motion where objects move along a straight line.
Examples: sprinters in race, falling stones etc.
(ii) Circular Motion : Motion where objects move along a circular path.
Examples: rotation of earth.
(iii) Rotational Motion : A type of circular motion where an object spins on its own axis, it is called rotational motion.
Example: rolling ball, spinning top etc.
(iv) Periodic Motion : Motion where the object repeats its motion after a fixed interval of time.
Examples: motion of swing, pendulum etc.

.png)
























.jpeg)


.jpeg)








.jpeg)
.png)

.jpeg)














.png)



